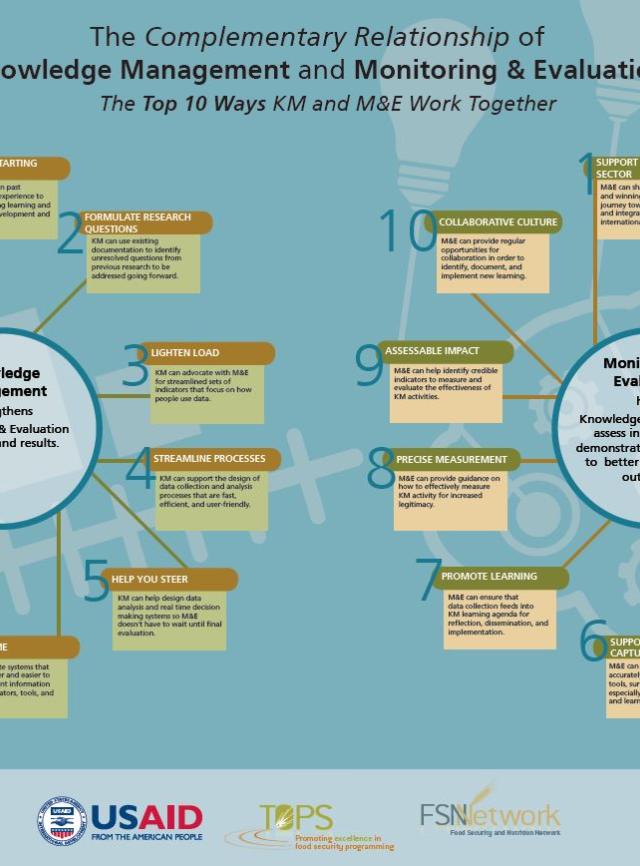
Adaptive Management
A curated collection of resources related to adaptive management and collaborating, learning, and adapting (CLA) relevant for emergency and non-emergency food security program implementers.

About this Collection
This is a collection of tools, case studies, templates, and other resources aimed at helping emergency and non-emergency food security program implementers to manage adaptively through continuous learning. Are you looking to use real-time data to inform activity pivots, conduct periodic pause and reflect workshops to better understand program successes and challenges, or facilitate a scenario planning workshop? Explore this collection of adaptive management and CLA approaches developed by the food security community and curated by IDEAL.
The resources are organized in alignment with the six components of USAID’s CLA Framework: Collaborating, Learning, Adapting, Culture, Processes, and Resources.
Introduction to CLA Collaborating Learning Adapting
Click the images to open the full graphic in a new tab.
Introduction to CLA
Collaborating, learning, and adapting (CLA) is a set of practices that help food security program implementers improve program effectiveness. The systematic application of CLA approaches enables implementers to design and implement programs that intentionally collect relevant qualitative and quantitative data, reflect on learning for adaptive management and program improvement, and then rapidly apply that learning to both operations and programming.
CLA in the Program Cycle: Collaborating
Effective internal and external collaboration promotes synergies, improves efficiency, and supports knowledge sharing and learning across traditional boundaries. It is foundational to locally led development. To collaborate effectively, activities need to identify the internal teams and external stakeholders whose input is necessary for informed planning and effective implementation. The where, when, what, and how influence the contributions—they matter! As a result, implementers need to build the skills within their teams to facilitate collaboration effectively and plan the details of collaborative opportunities. Collaborating sub-components: Internal Collaboration; External Collaboration
CLA in the Program Cycle: Learning
In every activity lies a wealth of learning opportunities. However, activity teams often face the challenge of identifying key learning priorities and establishing a consistent, systematic learning approach. To aid teams in this endeavor, donors and implementers have developed (and IDEAL has curated) many resources to: Harness technical evidence by tracking existing research, generating new research, and conducting pilots and evaluations; Develop, use, modify and share collaboratively developed logical theories of change; Design and implement M&E systems to collect high-quality and timely data to inform decision-making and facilitate continuous learning; Adapt to changing environments through preparing for changes in the operating environment, monitoring shifts, and responding promptly to ensure the activity’s seamless execution. Learning sub-components: Technical Evidence Base; Theories of Change; M&E for Learning; Scenario Planning
CLA in the Program Cycle: Adapting
Activities can improve impact by continuously and systematically documenting and using learning to inform decision-making, collaborating with stakeholders to analyze successes and challenges, and working with stakeholders to maintain, adapt or stop strategies and approaches as needed. Adapting sub-components: Pause and Reflect; Adaptive Management
Enabling Conditions: Culture
An organizational culture that supports continuous learning and improvement is essential to establishing CLA processes and behaviors. This kind of culture is built on trust and creates space for teams to problem-solve, innovate, and improve programming based on experience. Culture sub-components: Openness; Relationships & Networks; Continuous Learning & Improvement
Enabling Conditions: Process
To build organizational learning and support timely decision-making, technical, contextual, and experiential knowledge needs to be easily accessible to team members, when and how they need it. Team members must understand how decisions are made, be able to engage in relevant decision-making, and know when they have the autonomy to make decisions. Process sub-components: Knowledge Management; Institutional Memory; Decision-Making
Enabling Conditions: Resources
Staff with CLA-related skill sets and mind-sets are essential to effectively implement any CLA plan. When assembling a team, prioritize individuals with CLA-related skills and create opportunities for all staff to enhance their adaptive management capacity. Non-human resources—such as having flexible funds and agreement mechanisms—will further support effective CLA implementation. Resources sub-components: People; Other Resources